-

Smart Street Lights
Use Case Our use case is related to a new Smart Lighting Infrastructure, to be more adequate for a Traffic System which directly crossroad and our wasted time on those. The idea behind our project is to create models which should represent an actual Live Situation Crossroad. In the model there are different options creating […]
-

Smart Post – Sending Parcels
Use Case This project simulates the postal parcels sending service, this simulation consists of three use cases: Use Case 1: weight the parcel Use Case 2: fill in information, generate and print the QR-Code Use Case 3: validate the QR-code Experiment We don’t have enough environment and money to support the simulation of this project, […]
-
sIoT Cap2Comp & Comp2Cap
Use Case The aim of this project is to provide new functionalities for the s*IoT methodology. Basically, the idea is on the one hand to find out, which components are necessary for a given capability and on the other hand it should be also possible to figure out which capabilities can be used given a […]
-

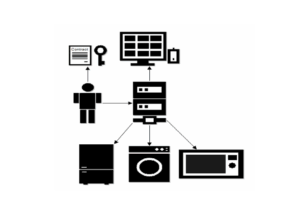
Smart-Home Supply Chain
Use Case The smart home supply chain scenario contains multiple use cases. The idea is to enable a smart supply chain inside a home. For that, the ESP32 sensors are being used (using the RFID). As a semantic technology Nools is being used (a JavaScript Version of Drools). In order to run this scenario, the […]
-
Scene2Model Extension
Use Case This project is an extension of the Scene2Model modelling tool. The aim of this project is to automatically provide a list of cars for a specific type of character (business man, worker etc.). The cars are selected according to the preferences of the selected character. The preferences are implemented in a turtle file and […]
-
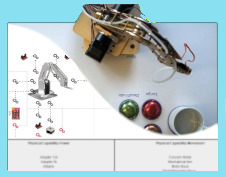
XST iRobot – OMiLAB Robotic Picking and Path Finding Experiment
Use Case The aim of this project is to provide a universal model based solution for automatic route planning and picking job execution in warehouse environments. Our research has shown that existing warehouse operations are typically performed by human beings. Related tasks are typically not mentally stimulating, repetitive, and exhaustive. Thus they can potentially negatively […]
-
ENERGY BLOCKCHAIN CONTROL
Use Case Due to the recent advances in household-level renewable electricity generation technology, a new type of market based on peer-to-peer (P2P) electricity trading between households will emerge. In this experiment we design a potential technical framework for energy controlling on a peer to peer network.Therefore, we set our focus on intuitive Use Cases that […]
-

CPS Environment Modelling
Use Case This project is based on the concept of “Smart” models and allows the creation of models that are easy to understand and reproduce for humans and at the same time can be read by a machine. It furthermore uses the starIOT framework which combines design thinking with Cyber Physical Systems (CPS). Recognizing use […]
-
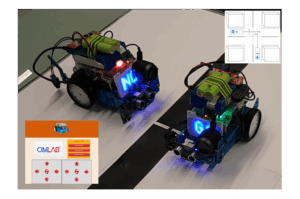
MBOT Collision Prevention
Use Case The Project is split into three different Use Cases which are: Experiment Use Case 1: The base concept of this use case is to create an environment where the MBOTs are able to move a certain distance in a certain direction. This could either be movement for a given distance, like for example […]
-
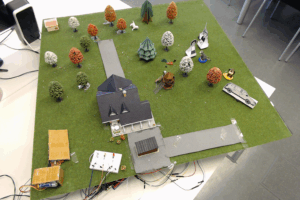
Smart Garden
Use Case My project is separated in three different location, which are typical for a domestic garden. Each location has different scenarios where some actions are triggered according to the presence of different agents. The agents are: an adult, a child, a postman, an autonomous car, a cat and a dog. The following scenarios have […]
-
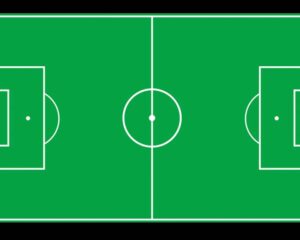
Image Recognition – Table Soccer
Use Case The aim of the project is to provide a system, which records and streams a table soccer game and analyses certain things in parallel and in real time. Its inputs are video data from cameras and acceleration data from suitable sensors. The outputs are details about the position of the ball and statistics […]
-
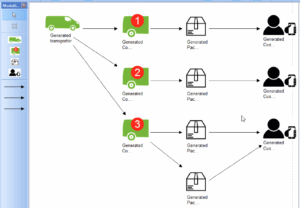
Smart Package Delivery with ADOxx
Use Case The aim of this project is to develop a modelling method with the ADOxx Metamodelling Platform 1.5 that supports automatic package delivery by providing models to manage and organize a self-driving vehicle and the packages which have to be delivered to the customers visually, as well as to calculate and display the most […]
-
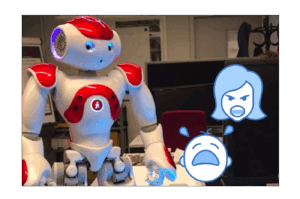
Sentiment analysis with NAO
Use Case In the near future intelligent robot assistants might become reality. Therefore, interactions between humans and computers are becoming more and more common. For robots to live alongside humans they need to possess some form of emotional intelligence. In this project we look at how we can utilize the information harvested from natural language […]
-

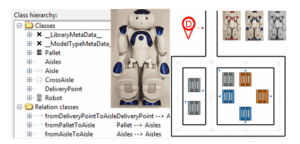
Robotic Order Preparation
Use Case A lot of processes are happening in an online grocery store. Some of them could be partly or even fully automatized. The focus of our OMiRob Case is on the automatization of the order preparation processes in an online grocery store’s warehouse using robotic workers. Therefore, it comprises parts of the ordering process […]
-
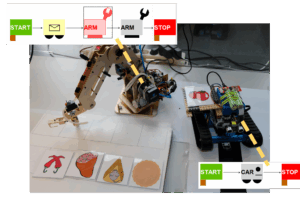
Delivery on Demand in a Cyber Physical System Production Line
Use Case Delivery on Demand in a production line by using a Makeblock Rover and a DOBOT RobotArm managed by a central controlling server system used with an ADOxx user interface Use Case Description (Making a pizza): Following a line, avoiding obstacles and placing products on the right place The DOBOT RobotArm is placing products […]
-
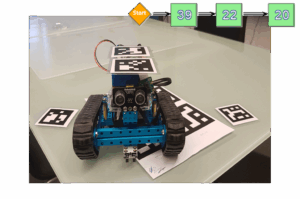
MBot Path Finder
Use Case MBot Path Finder has been developed by using the MBot Rover, the OMiTag Project and the ADOxx modelling interface Use Case Description: Following a path which is modelled in ADOxx, and recognizing objects at the reached destination The basic idea of the Project is to provide a system, which controls robots with the help of a […]
-
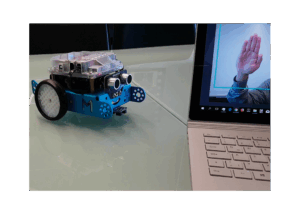
Gesture-based Interaction with Cyber Physical Systems
Use Case This project targets to implement a system that enables to control a cyber-physical-system (CPS) with gestures. The cyber-physical-system will utilize smart models to act autonomously. In our case a smart model refers to a knowledge-based model which can be processed by the CPS. Based on the gesture input the CPS receives, the CPS can […]
-
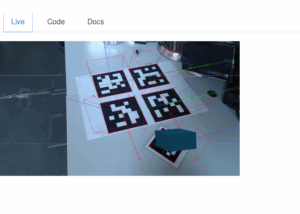
AR Playground
Use Case Make tag detection and AR Technologies more accessible by exposing them in a JavaScript-Based Development Environment. Project consists of multiple Subsystems: Code is available on DKE GitLab: https://gitlab.dke.univie.ac.at/OMiROB/OmiTagServer Future Work: Projected/Virtual Camera A Virtual “Projector” is created by using a shader to apply the video texture(s) onto a 3D-Surface.Scene Camera could then be […]
-
OMiLAB Robotic Spider Experiment 1
Use Case The use case is to create SVG image data and convert it into a drawing using the mSpider bot. The reason for using SVG images, is that they are both human and machine readable through the XML markup language that uses tags. It is easy to understand and edit the SVG file. Further, […]
-
CPS interaction with NAO
Use Case The goal of this project is to support the interaction between a person and a cyber-physical system with the help of the NAO. The NAO should serve as a smart assistant, which not only supports the interaction between a person and a CPS, but also helps the user to orient oneself within the […]
-
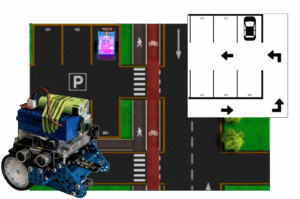
OMiLAB Robotic Car Experiment 3
Use Case The aim of this project is to provide an universal solution for a self-parking mechanism with autonomous parking place discovery. As a prototype vehicle served the Makeblock mBot. The mBot, similar to other, already adopted self-parking assistants by for example BMW and Audi, makes use of sensor devices, to gather information about the environment. The […]
-
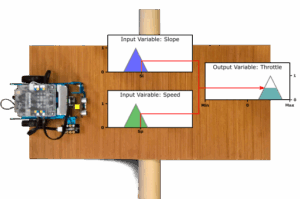
OMiLAB Robotic Car Experiment 2
Use Case To enable autonomous movement of robots, knowledge about its environment is necessary in order to coordinate appropriate movements. Since dynamic environments often lead to imprecise readings of the robot’s surrounding, knowledge representation schemes are required, which allow to handle fuzzy inputs. The aim of this experiment is to validate the use of fuzzy […]
-
OMiLAB Robotic Car Experiment 1
Use Case Use Case Description: Performing a Slalom The makeblock robot car called mbot should follow a black line on the floor till an obstacle appears in front of the car. The car should stop and avoid the obstacle. Afterwards it should continue following the line till the next obstacle appears and so on. Problem […]
-
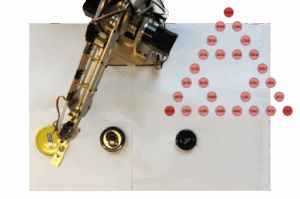
OMiLAB Robotic Arm & Car Experiment 4
Use Case This project is designed to enable the user to remotely play the puzzle towers of hanoi by interacting with a robotic arm. The use case is to solve this problem with three disks. While the user can interact with the game through the robo-arm and execute moves, the application can also autonomously find […]
-
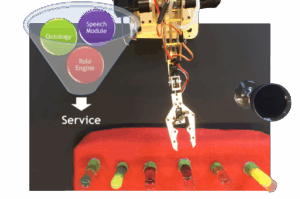
OMiLAB Robotic Arm Experiment 3
Use Case Scenario Mixing a cocktail with a Dobot arm by receiving speech input and subsequently incorporating the required ingredients. Flow of activities Move to ingredient ? grab tube ? move to cocktail glass ? tilt and empty the tube ? move to the center ? move to original ingredient position ? drop empty tube […]
-
Exploring Text-Based BPMN 2.0 Modeling at Bielefeld University of Applied Sciences
At the Bielefeld University of Applied Sciences, we are investigating innovative approaches to Business Process Model and Notation (BPMN) 2.0, focusing on text-based modeling techniques. In collaboration with our students, we have developed an initial prototype system that enables users to generate process models through natural language input, for example: “Please create a process model for…” This textual description […]
-
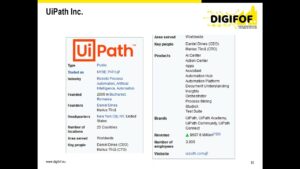
Robotic Process Automation – possibilities of practical applications
This experiment was developed as part of the EU project Digital Design Skills for Factories of the Future (DigiFoF). The project proposes a network of training environments where HEIs, enterprises and training insitutions come together to develop skill profiles, training concepts as well as materials for design aspects of the Factory of the Future (FoF). […]
-

Supervising and controlling White Wines Fermentation Parameters Evolution
Configurate a Neural Network and/or a Genetic Algorithm that can simulate the white wine fermentation Information This Web application implements the following main features: • User-customized Multi-Layer Perceptron (MLP) Neural Network (NN) • Meta-heuristic optimization methods for NN hyperparameters • Training and testing the tool based on experimental data • Graphical visualization and comparison for […]
-

Parking of a mobile robot using modeling languages
Information Creating a Hardware-Software application for: Streamlining traffic especially at peak hours, Reducing search time for a parking space, Reducing fuel cost with search for a parking space, reducing pollution and improving air quality.
-

Smart solutions for increasing the quality of plant life
Information The target of this experiment is to create a system of automating the irrigation process, using IoT (Internet of Things) technology to irrigate a garden. The system consists of two parts: a hardware part and a software part. The objectives are to monitor in real time the life of the plants, thus various parameters […]
-

Modelling and Simulation of an Automated System in an Agricultural Warehouse
Information The purpose of this application is to automate the activity in an agricultural warehouse. The assembly consists of a mobile robot (mBot) which has a video camera attached to the side of it, connected to the corresponding Raspberry Pi 4 module. The problem this assignment solves follows the scenario where a robot is walks […]
-

IoT System for Irrigating and Monitoring a Thuja Conifer Nursery
Information The target of this experiment is to improve the sprinkling irrigation process of a Thuja conifer nursery by monitoring the crops in real time. The aim is to find an optimal way of irrigation that guarantees a low volume of water used and an effective growth of the entire plantation. To achieve this goal, […]
-

Implementing an Embedded System to Identify Possible COVID19 Suspects Using Thermovision Cameras.
This work was developed under the project financed by Knowledge Transfer Center Hasso Plattner Institute at Lucian Blaga University of Sibiu. ICSTCC 2020 Presentation
-
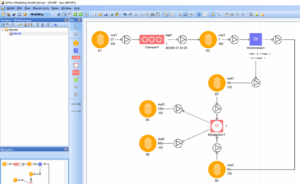
Digital Production Planner Tool
The flexibility of manufacturing processes is one of the major conditions for increasing the competitiveness of the factory of the future, in the current conditions of competition Design (modelling) tool for the Factory of the Future Modelling Toolkit The modelling tool that implements the concept of modelling method presented in [D3.3] we called it the […]
-

Digital design of food manufacturing processes
Introduction to modeling and simulation using Petri Nets, modelling and simulation of food manufacturing processes, digital design manufacturing processes Digital Methodology and Tools in Factory of the Future C5 Digital design of food manufacturing processes theory and applications C5 Digital design of food manufacturing processes theory and applications Video Video Video Video Video Video Video […]
-

AI – an essential tool for control process in food engineering education
AI – an essential tool for control process in food engineering education. Implementation the inquiry based approach method using simulation based learning in teaching process control Teaching process control in food engineering AI in teaching process control Simulink_diagram_control_loop Process_test_method
-

Automation of assembly lines assisted by a robotic arm and a mobile robot
Simulation of assembly line automation using modeling languages. Handling a robotic arm and a mBot
-

User Centric Services to Introduce AI into Companies
User Centric Services are simple-to-use services that provide a bundled collection of features to the user without the need that the user is in contact with the full-fletched and hence complex model-language, tool functionality or integrated services. Such user centric services will be developed to support the AI readiness assessment, identify suitable AI algorithms, the […]
-
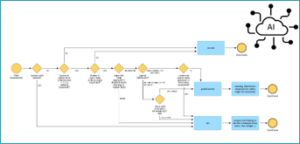
Service to Extend Process Modelling for domain-specific AI
To complement “self-configuration” and “self-learning” BOC is offering consulting and configuration support during the digital transformation of production processes. The consulting is offered in combination with process modelling tools. IPR / Licence IP: Authorship/Copyright License: Commercial Contact Person Robert Woitsch Information More information is provided in: Use The following Video shows workflow definitions created based […]
-

OLIVE Microservice Integration Framework
The OLIVE Microservice Integration Framework is a low code platform and enables the “self-configuration” of model-based decision support and management frameworks. Applications, sensors and services can be integrated using smart and reliable technologies like meta modelling, workflows and data mappings into full fletched management systems. IPR / Licence IP: Trademark License: Commercial Contact Person Robert […]
-

InterOperabaleDataHub
Responsible Partner: JOTNE The InterOperableDataHub addresses critical data challenges in industrial settings: data integration, vendor lock-in due to proprietary formats, and long-term archiving. This solution leverages Jotne’s EDMtruePLM™ platform to act as the central Knowledge Base. Built on international standards (ISO STEP), it ensures interoperable and trustworthy data storage across design, production, and operations, supporting […]
-
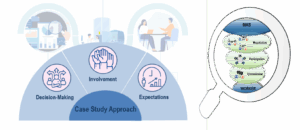
Democratization in Industry via MAS: Case Study Approach
Responsible Partner: RWTH Aachen University AI-based decision support systems create new opportunities for decision-making and co-determination in companies, raising the question of whether and how democratization can take place in this context. To explore this, we introduced a conceptual approach for analyzing democratization efforts and examined specific challenges through a case study of an SME. […]
-
Innovation Shop Modelling
Responsible Partner: OMiLAB The FAIRWork Innovation Shop is an online platform, where the partners of the FAIRWork project upload there achievements in the form of self-contained innovation items, meaning that they can be understood and used without the need for a broad knowledge of the FAIRWork project. In this context, this innovation item contains a […]
-
Innovation Shop
Responsible Partner: OMiLAB The Innovation Shop Portal hosts key facts and description of research and innovation results from the project, as well as, eventually description and reference to the source of generic and re-useable functional parts. It provides additional descriptions and demonstration samples, to communicate the innovations with potential users, to enable the re-use of […]
-
Experimentation Module
Responsible Partner: OMiLAB The Digital Innovation Environment powered by OMiLAB contains a model-based approach and an environment to create experiments to analyse and evaluate innovative ideas. The goal of the innovative idea is defined in concrete scenarios, which are used as one input for the experiments. The other input is the abstraction of the environment, […]
-
Design Thinking Workshop
Responsible Partner: OMiLAB OMiLAB offers facilitation for design thinking workshops with Scene2Model. In order to hold successful workshops, they need to be prepared and a guided. OMiLAB offers the facilitation for workshops based on an established methodology, which supports the preparation, the physical workshop itself and supports the post processing of the information created in […]
-
Scene2Model
Responsible Partner: OMiLAB Scene2Model is an environment for supporting physical design thinking workshops based on paper figures, by offering an environment for automatically creating digital models out of the physical models. These digital models are usable during and after the workshop, where the represent the created idea for humans, based on their semantically rich representation. […]
-
IoT Innovation Space Consulting Service
Responsible Partner: JOANNEUM RESEARCH The IoT innovation space is is both a physical and virtual space equipped with IoT tools (e.g., low-cost sensors, gateways, RFID/NFC tools) to explore the development and design of AI methods and optimization techniques, as well as to demonstrate the benefits of these data-driven IoT techniques for decision-making. The goal is […]
-

Consulting Services with Human Factors Lab for Production Environments
Responsible Partner: JOANNEUM RESEARCH Services of knowledge engineering about human psychophysiological strain in production environment including service with sensor-based measurement technologies. The Human Factors Lab combines state-of-the-art wearable, mobile and stationary measuring technologies with innovative analytical software for conducting human-centred studies and developing advanced prototypes. The lab provides Digital Human Factors Analytics focusing on human […]
-
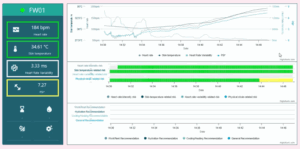
Intelligent Sensor Box
Responsible Partner: JOANNEUM RESEARCH A framework for the integration of a set of stationary and wearable sensors and AI-based analytics with optimisation functionality for worker based assessment of psychophysiological strain This tool enables to digitally measure and monitor workers’ and decision makers’ Human Factors, such as, stress, in real-time while doing tasks. It consists of […]
-
Optimisation Toolbox
Responsible Partner: JOANNEUM RESEARCH This is a toolbox with a set of optimisation algorithms using different techniques ranging from AI to mathematical optimisation. These software services are broadly focused on industrial optimisation challenges in the areas of manufacturing and healthcare. In general, they are designed to solve difficult problems in the areas of allocation, scheduling […]
-

Process Maestro
Responsible Partner: MORE CoLAB Process Maestro is a practical tool designed to assist businesses in managing and improving their workflows more effectively. The main aim of Process Maestro is to help organizations adapt and refine their processes in response to dynamic operational needs. It encourages a collaborative approach by promoting increased participation from stakeholders, supporting […]
-
AI Models Research and Development
Responsible Partner: RWTH Aachen University WZL-IQS of RWTH Aachen University specializes in developing customer-tailored AI models, leveraging deep expertise in data-driven methods such as data analysis, Machine Learning, Reinforcement Learning, and Deep Learning—particularly in manufacturing. This expertise is one of our greatest assets, enabling us to deliver significant value to our customers. Additionally, we provide […]
-
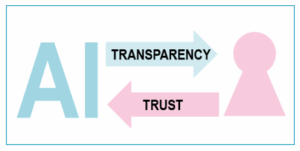
AI Transparency for Trust
Responsible Partner: RWTH Aachen University To ensure AI systems are reliable and trustworthy, they must be tailored to human needs rather than forcing humans to adapt to technology. Users trust AI systems when they function effectively and operate correctly, which requires transparency regarding performance and underlying mechanisms. This aligns with the European Commission’s requirements for […]
-

Production Decision Support
Responsible Partner: FLEX Supporting of Flex trails and simulation of FairWorks tools -after Evaluation and success implementation in factory environment. Find more information at: https://innovationshop.fairwork-project.eu/items/6/
-

Success Stories
Responsible Partner: CRF Hosting and operation of the CRF trials, and the opportunity to integrate the FAIRWork components and platform for its testing and validation Find more information at: https://innovationshop.fairwork-project.eu/items/5/
-

EDMtruePLM™
Responsible Partner: JOTNE Product Data Management system based on Open Standards (ISO/TC184/SC4, ISO 10303, STEP). EDMtruePLM is a product model server for integrating, storing, and accessing data for type of products and for individual products over their lifetime in a standards compliant fashion. It supports Digital Twins – CAD, CAE/Simulations, PLM and sensor data (IoT) […]
-

User Centric Services to Introduce AI into Companies
Responsible Partner: BOC User Centric Services are simple-to-use services that provide a bundled collection of features to the user without the need that the user is in contact with the full-fletched and hence complex model-language, tool functionality or integrated services. Such user centric services will be developed to support the AI readiness assessment, identify suitable […]
-
Service to Extend Process Modelling for AI
Responsible Partner: BOC To complement “self-configuration” and “self-learning” BOC is offering consulting and configuration support during the digital transformation of production processes. The consulting is offered in combination with process modelling tools. Find more information at: https://innovationshop.fairwork-project.eu/items/2/
-

OLIVE Microservice Integration Framework
Responsible Partner: BOC The OLIVE Microservice Integration Framework is a low code platform and enables the “self-configuration” of model-based decision support and management frameworks. Applications, sensors and services can be integrated using smart and reliable technologies like meta modelling, workflows and data mappings into full fletched management systems. Find more information at: https://innovationshop.fairwork-project.eu/items/1/

Explore the experiments of the
OMiLAB Community of Practice
The following experiments are realized within the project








